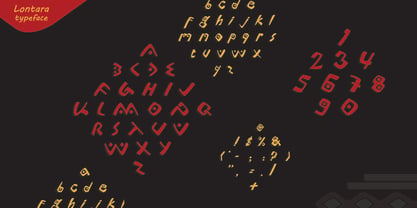10,000 search results
(0.064 seconds)
- Bonbon Bleu - Unknown license
- Honey Florist - Personal Use - Personal use only
- BILLY ARGEL FONT - Personal use only
- JANDA Love And Rain - Personal use only
- Selfish - 100% free
- War Letters - Personal use only
- LYSSA DEMO VERSION - Unknown license
- Stefan Budde-Siegel - Personal use only
- Moeflon - Unknown license
- Life-Lessons - Personal use only
- Venice Classic - Unknown license
- LostWages - 100% free
- LT Beverage - 100% free
- Yasuragi by Hanoded,
$15.00Yasuragi means ‘Peace of Mind’ or ‘Tranquility’ in Japanese. It is something I do not have a lot of since the corona lockdown…the ;-) Yasuragi is a handmade script font. It is quite neat, quite elegant and quite useful (in a tranquil, peace-of-mind kinda way). Yasuragi comes with double letter ligatures and all the diacritics you want. - Ongunkan Phoenician by Runic World Tamgacı,
$50.00Phoenician/Canaanite The Phoenician alphabet developed from the Proto-Canaanite alphabet, during the 15th century BC. Before then the Phoenicians wrote with a cuneiform script. The earliest known inscriptions in the Phoenician alphabet come from Byblos and date back to 1000 BC. The Phoenician alphabet was perhaps the first alphabetic script to be widely-used - the Phoenicians traded around the Mediterraean and beyond, and set up cities and colonies in parts of southern Europe and North Africa - and the origins of most alphabetic writing systems can be traced back to the Phoenician alphabet, including Greek, Etruscan, Latin, Arabic and Hebrew, as well as the scripts of India and East Asia. Notable features Type of writing system: abjad / consonant alphabet with no vowel indication Writing direction: right to left in hortizontal lines. Sometimes boustrophedon. Script family: Proto-Sinaitic, Phoenician Number of letters: 22 - there was considerable variation in their forms in different regions and at different times. The names of the letters are acrophonic, and their names and shapes can be ultimately traced back to Egyptian Hieroglyphs. For example, the name of the first letter, 'aleph, means ox and developed from a picture of an ox's head. Some of the letter names were changed by the Phoenicians, including gimel, which meant camel in Phoenician, but was originally a picture of a throwing stick (giml). - Fournier by Monotype,
$29.99Fournier was made by Monotype in 1924. The design is based on types cut by Pierre Simon Fournier circa 1742, some of the most influential designs of the eighteenth century. Fournier's types were among the earliest of the transitional" style of typeface and were a stepping stone to the more severe "modern" style made popular by Bodoni later in the century. They had more vertical emphasis than the old style types, greater contrast between thick and thin strokes and little or no bracketing on the serifs. Fournier has a light, clean look on the page, provides good economy in text and retains an even colour. - Lontara by Triden Works,
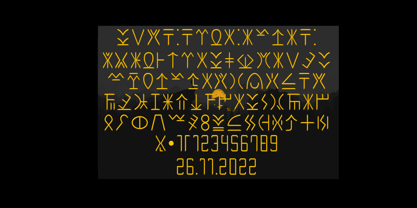
$21.00PREFACE Lontara typeface shape is originally created by freehand technique, without modify other exist digital typeface. It purely inspired by traditional Lontara manuscript, South Sulawesi. Lontara typeface is dedicated for originality of Indonesian Cultural. ORIGINS The La Galigo that written in traditional Lontara script is widely believed by people Buginese as a bible of sacred and should not be read without a certain ritual preceded.It tells the story of hundreds of descendants of the gods who live at a time for 6 (six), hereditary generation, the various kingdoms in South Sulawesi and the surrounding islands. The Lontara script is an Brahmic script traditionally used for the Bugis language, Makassarese language, and Mandar languages of Sulawesi in modern Indonesia. It is also known as the Buginese script. It was largely replaced by the Latin alphabet during the period of Dutch colonization. - Ongunkan Cypriot Linear C Sylla by Runic World Tamgacı,
$100.00This font is an adaptation of the cyprus syllabic script to a Latin-based font. I tried to assign as many correct letters as possible, but there were too many characters so I had to fit them. Please review the alphabet table of Cypriot syllabic to use the Font. To see all the characters, you can see all the characters and add them to the text by selecting this font from the add character section on the word page. Cypriot syllabary The Cypriot syllabary was used in Cyprus from about 1500 and 300 BC and is thought to have developed from the Linear A. The earliest known inscriptions from between 1500 and 1200 BC are in an unknown language called 'Eteo-Cypriot', or 'True Cypriot', and the script in which they are written is called Cypro-Minoan. From around 1200 BC Cyprus began to be colonised by Mycenaean, Minoan and possibly Cretan Greek settlers, and they probably adapted the existing script to write their own language - the oldest known inscription in Greek dates from the 11th century BC. Cypriot Greek had much in common with Greek dialects of Arcadia and Pamphylia, which corresponds to the province of Antalya in Turkey. - Konditorei by Hanoded,
$15.00A Konditorei is a German Confectionery Shop. A good Konditorei offers a wide variety of pastries and often also serves as a café. This handmade script font is like the wares in a confectionery shop: full of calories, but sweet and delicious. Use it for your food blogs, your magazines and product packaging. Comes with heaps of diacritics and ligatures for double letters. - Formosa by Hanoded,
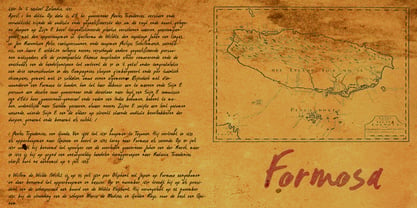
$15.00Formosa is the old, colonial name for Taiwan. Formosa means beautiful in Portuguese and I think this handwritten typeface has a certain beauty itself. It comes in three styles, all of which make extensive use of ligatures, to give the font an authentic, handwritten feel. Like most of my fonts, Formosa comes with Babylonian language support. - Bloemche by TypeThis!Studio,
$54.00It's spring time and this is our tribute to the wonderful city of Colonia! Bloemche is a warm-hearted display serif font combining a set of floral symbols with an extravagant semi-script style. It is perfect for blogging a revitalizing style into the loveliest season. Create floral typography dreams and socialise with the people around you. Enjoy yourself! -- Typeface Features 711 Glyphs 45 Stylistic Alternates 6 Styles: Regular, Medium, Bold, Extra Bold, Black, Flowers Full Latin Language Support Numerators/Denominators Sub- and Superscript Fractions Ordinals Standard Ligatures Slashed Zero - Winnetka JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00Winnetka JNL was inspired by Cooley Antique Tuscan Condensed - a printer's wood type manufactured in 1859 by J.G. Cooley. Given an additional hand-made treatment, the lettering resembles characters made from cut paper. - Lila Pro Heavy by Eurotypo,
$27.00The Lilac (or Syringa vulgaris), a slightly vigorous plant, gives a nice colour to the place where its located, well maintained from one season to another and even when not in flower, the colour of its foliage and compact form makes it attractive enough. Lila Pro was created on the coast of Andalucía, inspired by its vibrant colour’s contrasts, and lush climate. This new script has all the advantages of OpenType technology that allows a variety of combinations: standard ligatures, contextual alternates, discretional ligatures, word ending and tails. Specially designed for creating logos for products and packaging, this font can also be used as body text for its good legibility and accurate kerning. - Blonde Personal Use - Personal use only
- Billund by Elster Fonts,
$24.00Have you ever played with Lego™ and built letters? With Billund Side and Billund Top you can do it again and create colourful headlines on your Mac or PC. Billund is a font-system consisting of the two base-fonts Billund Side Outline and Billund Top Outline, extended by layer-fonts for one or five colours. Use the Outline-fonts alone to get »transparent« letters in one colour, use it with the Fill-fonts to fill the whole letter with one colour, or use the five Colour-fonts to get colourful letters in every colour you want. Billund contains cyrillic and greek glyphs and can be used for nearly a hundred languages. To expand the typographic possibilities, small caps, old style figures, numerals for small caps (c2sc), three stylistic sets, different symbols, forms, standard- and discretionary ligatures have been added, furthermore contextual alternates to avoid colliding letters. Each Billund-font contains 870 glyphs and more than 1600 kerning-pairs. Billund is named after the city of Billund (Denmark), where Lego™ was invented, the Lego™-headquarter still resides and the first Legoland™ theme park was opened in 1968 and still exists today. - Good Sport JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00Good Sport JNL has nothing to do with any of the major sports activities such as baseball, football, basketball or soccer. Instead, the typeface gets its name from the sport of camping, as the lettering was spotted on an image of an old ad for the Colonial Forest-Master boy’s pocket knife. Good Sport JNL is available in both regular and oblique versions. - Bonhomme Richard by Three Islands Press,
$39.00Bonhomme Richard evokes the cursive penmanship of Chevalier John Paul Jones (1747–1792), celebrated Continental Navy commander during the American Revolution, in letters from the late 18th century. The font’s name comes from Jones’s famous frigate, lost during his victorious engagement with the British in the Battle of Flamborough Head in 1779. During this battle Jones is said to have exclaimed, when urged to surrender, “I have not yet begun to fight!” (In fact, his likely words were, “I may sink, but I’ll be damned if I strike!” – i.e., surrender.) A legible script, Bonhomme Richard has an elegance about it while also conjuring the colonial era of its source material. Use to simulate historical handwriting in film props, games, formal invitations, product labels, and the like. - AlphaRev Hollow - Unknown license
- Intellecta Bodoned by Intellecta Design,
$15.95a complete family of Bodoni style inspired typeface - Barnette by Black Studio,
$15.00Barnette Script is a new modern script font with an irregular baseline. Feminine style and style.Barnette Script looks beautiful on wedding invitations, thank you cards, quotes, greeting cards, logos, business cards and more. Perfect for use in ink or water-colour. Includes start and end letters, alternatives and support for many languages. To activate the OpenType Stylistic alternative, you need a program that supports OpenType features such as Adobe Illustrator CS, Adobe Indesign & CorelDraw X6-X7, Microsoft Word 2010 or a later version. There is an additional way to access alternatives / swashes, using the Character Map (Windows), Nexus Fonts (Windows), Font Book (Mac) or a software program such as PopChar (for Windows and Mac). - China - Unknown license
- AlphaRev - Personal use only
- Otari by TK Type,
$25.00Otari is vibrant and contemporary, but serious and built to last. Its character shines in display type, but doesn’t interfere at text sizes. Otari aims to capture the essence of Wellington, New Zealand in a single typeface. The contrast of a colorful art scene and the conservative colonial British aesthetic, which is still evident in the capital city, laid the groundwork for this design. - Libertinas-co. - Personal use only
- Lovely Amatis Signature - Personal use only
- Don Quixote - Personal use only
- Dirty and Classic - Personal use only
- Posteratus Rex - Personal use only
- Remeslo - Unknown license
- PreludeFLF - Unknown license