10,000 search results
(0.031 seconds)
- Marvin by Canada Type,
$29.95The objective of this font was to try and find out how far back in the designer's life this obsession with letters began. The challenge was to draw, from memory only, two sets of caps that recall older Looney Tunes and Merrie Melodies lettering. The experiment was a success, which means that the designer's got it bad since he was, like, four! The Marvin set includes three stylistic variations (Regular, Round and Shadow), with extensive multi-script language support covering Western, Central and Eastern European languages, as well as Cyrillic, Greek and Vietnamese. A few extra alternates and interlocking ligatures are also included, all adding up to over 650 characters in each font. And here we are. Marvin is a great cartoon font that can help you build your very own Illudium Q-36 Space Modulator, so you can trigger that earth-shattering kaboom. Then you're on your way to claim this planet in the name of Mars. Isn't it lovely, mm? - 57-nao by ILOTT-TYPE,
$49.00Designed in 1950s Japan by Okanao & Kushiro, the perfect partnership until artistic temperaments drove them apart. The duo spent years crafting the font with the working title “Messenjā”, Okanao bringing technical expertise to craft letterforms, while Kushiro made it his life, obsessively working late into the night to check pages for errors. For him the project was never about making money, it was an artistic endeavor to reprint the great Western works of literature. When he found out Okanao had secretly sold the rights to the font for use as a logo for a major Japanese manufacturer, Kushiro burned all evidence of the designs in a fit of passionate fury. The two reportedly never spoke again. “Messenjā” was thought lost forever until a type specimen was discovered in a vintage typewriter box bought on eBay. Now redrawn and available as 57-nao, a faithful and beautifully crafted monospace characterized by what is considered Okanao’s defining moment, the angular loop on the lowercase ‘a’. - Publica Sans by FaceType,
$-Publica Sans is a clean geometric typeface, equipped with a variety of OpenType features to give you all you need for great typography: Alternates, arrows, rare currency symbols, case sensitive forms, various sets of figures and discretionary ligatures. Publica Sans has two sisters: Publica Play and Publica Slab Take a close look at our gallery (especially ‘OpenType Features 1–6’) to discover the versatility of Publica Sans. Alternates Give your typography a certain spin with the variety of alternate letters provided. Currency You need to set prices in exotic countries? No problem: Publica Sans gives you loads of rare currency symbols. Case Sensitive Forms Sometimes you write in all caps and there are some symbols (e.g. brackets) that need some extra treatment to make it look perfect – that’s what case sensitive forms are for. Figures Publica Sans provides 6 sets of figures, like lining, tabular, oldstyle, numerators ... Discretionary Ligatures Ligatures can make your logo or headline look spicy. So there are plenty of them. - Silent Noise Font Duo by Dora Typefoundry,
$19.00Silent Noise has two font types, namely serif and handwritten script with a thin size, adding to the impression of elegance and class, both of these fonts have a subtle touch Silent Noise is versatile enough to add an elegant element to almost any project that requires a special touch of class.,perfect for casual type on greeting cards, illustrations, quotes, old branding, cover books, social media posts, packaging and many others :) Features : Uppercase & lowercase Numbers and punctuation Alternates & Ligatures Multilingual PUA encoded WHAT'S INCLUDED Silent Noise Serif Silent Noise Script Once you download this romantic, handwritten font duo you will be able to start creating straight away. Enjoy! We highly recommend using a program that supports OpenType features and Glyphs panels like many of Adobe apps and Corel Draw, so you can see and access all Glyph variations. This type of family has become the work of true love, making it as easy and fun as possible. I really hope you enjoy it! Thak you. - Bach by Los Andes,
$39.00We have grown a new flower in our Garden, but this time, in a more emotional way, capturing its vibrations and using them to create a fresh handmade typeface: ‘Bach’, a display type system inspired by the new lifestyle trends that look to go back to basics and increase the value of old natural healing methods. Bach comes in two styles: a 6-weight Serif font in regular and italic versions, and a 2-weight Script in regular and bold versions. Ornaments are also included! Bach Script is based on the calligraphic catchwords set (handcrafted with brush pen) and the Serif version of the Garden typeface. This font is the perfect choice for labelling, packaging, illustrated books and posters. Go back to nature and feel the vibration again, this time with Bach! Bach is a Mendoza Vergara Studio design with the collaboration of Cecilia Mendoza in digital editing, under the supervision of Luciano Vergara and Coto Mendoza. - Tessie Letters by Ingrimayne Type,
$8.00A tessellation is a shape that can be used to completely fill the plane—simple examples are isosceles triangles, squares, and hexagons. Tessellation patterns are eye-catching and visually appealing, which is the reason that they have long been popular in a variety of decorative situations, such as quilting. The TessieLetters fonts contain letter shapes that can be used to construct tessellation patterns. Each family has two styles, an outline style and a filled or black style. The black style can be used to construct colored patterns. To see how patterns can be constructed, see the files here for TessieLettersACE, TessieLettersFQ, TessieLettersGJKMN, TessieLettersLL, TessieLettersTT, TessieLettersOSZ, and TessieLettersSingles. Many or these patterns were discovered/created by the font designer during the past twenty years in the process of designing maze books, coloring books, and a book about tessellations. The TessieLetters are picture or dingbat fonts. For fonts of tessellating letter shapes that can be used for text, see the Tescellations family. - Silver Streak by Swell Type,
$20.00Inspired by the streamlined lettering of trains, cars and advertisements from the 1930s and 1940s, Silver Streak is a font family that combines Art Deco elegance with refined craftsmanship and modern features. Silver Streak's contrasting strokes and tastefully rounded corners conjure an era of refined, vintage elegance. An extravagant palette of 25 weights — from gracefully tall and thin to commandingly wide and heavy, along with a variable font for unlimited options between — provide unforgettable branding possibilities for luxury items ranging from jewelry, clothing and perfume to the sleek badges of high performance sports cars. Features: Five widths from Compressed to Extended Each with five weights from Light to Heavy Complete family includes a Variable font for precise control of weight and width Support for 223 languages, including Western & Central Europe, Russian Cyrillic, Serbian/Macedonian, Ukranian and Vietnamese Alternate hook-cornered capitals (accessible as Opentype Discretionary Ligatures) Alternate round-topped A in two versions, each with international accents (accessible as Stylistic Alternates) - Falling Richees by Zamjump,
$21.00Falling Richees is a handwritten script with authentic dry brush imperfections. Falling Richees has a final letter combination to get the look you want :), besides Falling Richees also has a swash combination, to be placed under the writing you made, this is very easy to use, because this feature I intentionally made as an alternate type of letter lowercase. (see the example in the preview image) No special software is required to access any of the standard or alternative fonts - additional letters are provided in two forms 1. ending swash, 2. line swash :) WHAT IS INCLUDED: Falling Richees.ttf Multi language Ending swash Line swash For people with opentype-capable software: The alternatives can be accessed by turning on the 'Alternative Style' and 'Ligatures' buttons in Photoshop's Character panel, or through any software with a glyph panel, e.g. Adobe Illustrator, Photoshop CC, Inkscape. I hope you have fun using Falling Richees ! Happy creative! - FWD Egyptian Tower by Fontwright Design,
$39.99FWD Egyptian Tower is a designers stack-able Display family best purchased as one package. The four versions can be manipulated in your favorite graphics or sign making application to achieve the different effects as shown in the font family ad designs. All fonts are tightly spaced and are very often intentionally overlapped creating a balance for each very unique wider bottomed character. Being stack-able, the designer can duplicate the original text layer and by changing the font on the lower of the two layers to another of the family can then add another available effect. This can be repeated to add other of the available effects. Then by converting the text of the lower text layers to curves or outlines and welding the characters of the words together, the overlaps can be eliminated. This process is fairly common practice for a graphic designer and quite easy once done a few times. - Deus by Renegade Fonts,
$22.00Deus is when type design is brought to extreme. It tries to answer the question whether you can design all glyphs in one axis of stress. It does not try to be all purpose, useful at all sizes, legible or readable and most of all it does not try to be neutral. It has its own style you either accept or not. But if you do so, it has many great stuff inside. Every glyph has the same width across four masters, so you can change the style in one title or even make an animation out of that. It also has some cool animated emojis, so make sure you take all four styles! Deus has two sets of styles. "Deus" that has an expanded glyph set, and "Deus Basic" that comes with a limited glyph set. You can play around with "Deus Basic" since you get it for free, then fall in love with this font family and go for the full version. - Vertrina by Greater Albion Typefounders,
$8.95Vertrina marries four virtues: elegance, simplicity, character and usefulness. It started as an idea to combine two things: the elegance of classical Roman typefaces and of classical Roman architecture. The result is that rarest of all things - a truly new face that is elegant yet characterful but not so obtrusive as to be restricted to display work. All the faces' uprights mirror the elegant taper of Roman columns, as used in the most simple and elegant form of Roman architecture. The serifs are a subtle shape that mirrors the pediments and corbels of that same order of architecture. Vertrina is a family of eight faces, four upper and lower case faces, suitable for the elegant setting out of text, and four small capitals faces ideal for headings and titles. You'll find regular and bold weights and normal and condensed width, as well as a range of Opentype ligatures. All faces are offered individually and in family groups. Bring some simple elegance to your work. - Swonderful by The Ampersand Forest,
$19.00Everyone loves an Art Deco typeface. And there are hundreds of similarly-designed deco faces out there! But not one of them seems to have every form of every character that you want or need at any given moment. That’s why Swonderful was created! It has more letterform variations than you can shake a stick at (if you're inclined to shake sticks at things). With four variations of every uppercase form, two variations of every lowercase form (plus diacritical characters for the standard set), you’re bound to find the character you need for any given project, whether the style is French Art Deco, American Streamline Moderne, or Jazzy Midcentury Gaspipe. Just switch between stylistic sets! And you’ll find all those characters in three standard weights: Light, Regular, and Bold. They’re designed as a unicase, so they’re all height-compatible, and every set works with every other set, so you can mix and match to your heart’s delight! - Grantig by Julien Fincker,
$19.99Grantig is a bold serif display typeface. Inspired by the opening titles of old western movies, the genre of western slab serifs has been translated into a modern context and adapted to today's needs. As a result, it breaks free from the chains of its genre and opens up to many themes. Grantig is the german word for grumpy. With its massive serifs and strictly rounded curves, it comes particularly close in character to the grumpy Western heroes of days gone by, always in the presence of his two leaning companions, Slant and Backslant. With Grantig, it is particularly easy to create eye-catching and type-accentuated headlines. Its expressive nature makes it particularly suitable for editorial, packaging and advertising. With its 482 characters, Grantig covers the language usage for many Latin-based languages. At the same time, it has the most important open type features, such as lining and oldstyle figures, alternate characters, and arrows. - Extra Old by Mans Greback,
$59.00Extra Old is a vintage serif typeface. With heavy strokes and miniscule serifs, this classic font family is the perfect lettering for a headline to emit genuine quality. Why not use Extra Old for a traditional logo or balanced product label. Created with pride and care, this type has the optimal appearance of a classic vintage logo but for a modern setting. The font family consists of Regular and Italic, as well as Bold and Bold Italic. Also included are the font styles Coaster and Floria Corner, two typefaces for beautiful decorative elements, combining with the lettering. The font is built with advanced OpenType functionality and has a guaranteed top-notch quality, containing stylistic and contextual alternates, ligatures and more features; all to give you full control and customizability. It has extensive lingual support, covering all Latin-based languages, from Northern Europe to South Africa, from America to South-East Asia. It contains all characters and symbols you'll ever need, including all punctuation and numbers. - XXII CoolScript by Doubletwo Studios,
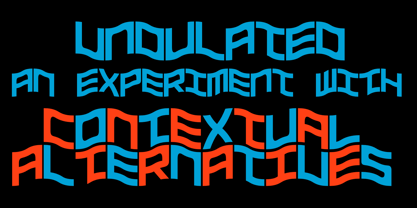
$25.99XXII CoolScript - The vibrant typeface with a ton of alternates MAJOR UPDATE This is a big update of XXII CoolScript. First of all, from now it’s a whole family with 7 new weights from ExtraThin to Black. It comes with more than hundred additional glyphs, some more alternates, ligatures, numerals and fitting opentype features for fractions and two extra ampersands. This lovely script font by Lecter Johnson is another, more soft and round one in the series of Doubletwo Studios’ script fonts (XXII YeahScript, XXII AwesomeScript). Its wonderfully designed letters, ligatures and alternates may bring a charming and individual handwritten look to your creation. This fonts are designed to easily create logos, headlines and text phrases within a blink of an eye. Just open your glyphs-palette* and simply chose, from up to 27 different alternates and variations per glyph, the one that fits best for your needs. *For further information visit the Behance Project. - Undulated by Ingrimayne Type,
$10.00Undulated is another typeface family from IngrimayneType that explores the possibilities of alternating letters sets. Undulated is similar to the typeface Undulate. Both alternate two sets of characters to form a wavy line of text. This alternating is done automatically in applications that support the OpenType feature contextual alternatives (calt). However, the peaks and valleys of the wave are in the middle of the characters in Undulate while in Undulated the peaks and valleys are at the right and left edges of each character. The waves in Undulated seem more chaotic and less soothing than the waves in Undulate. Undulated has monospaced and monoline letters. The letter spacing is tight to accentuate the ripple pattern. The family includes an outline style that can be used in a layer above the regular style to add color. The unusual patterns that Undulated gives are eye-catching and may be useful for advertising or signage and in other places where one wants attention-grabbing lettering. - Balcony by Shaily Patel,
$10.00Balcony is a decorative display typeface inspired by the patterns of metal safety grills. Its highly geometric features may be used to identify it as Art Deco. It is a monospaced type family with all characters confined in a square frame. The main idea of Balcony is to create a grill-like pattern when letterforms are placed together. This creates an illusionary experience for the reader. The best way to use this typeface is without leading, as shown in the visuals. Balcony also comes with two stylistic sets. The first stylistic set contains most characters with more decorative elements and the second one includes Dingbats. These Dingbats are motifs with simple geometric patterns that may be used for any kind of ornamentation. The diacritics letterforms are geometrically squeezed within the square frame to include the accents. This experimental typeface comes with about 650 characters and four weights (Thin, Light, Regular and Bold). The font family supports Western and Central European languages. - Alfons by Fenotype,
$35.00Alfons is a handy collection of 38 display fonts with a pack of Ornaments and Extras on top of that. Alfons is great for any kind of display use from online to packaging to posters or identities. Alfons is divided into eight subfamilies that play great together. Alfons’ core family is a monoline script that has eight weights from extra thin to black and on top of that two printed versions that have softer, a bit blurred features. Alfons Script is equipped with Standard Ligatures which makes the flow more natural. For more swirling swashes and bouncy flow try Swash, Stylistic or Titling Alternates in any OpenType savvy program or manually select from even more alternate characters from Glyph Palette. Alfons Display, Sans, Condensed, Serif and Slab are equipped with Swash alternates and Alfons Tiki has interlocking ligatures feature that you can access from Discretionary Ligatures. Alfons Extras is a pack of pictograms and icons and some catchwords. Alfons Ornaments is designed to work with Script. - Brighten by Eurotypo,
$22.00Brighten is the new family font composed of Brighten Regular and Regular Italic, Brighten Round and Round Italic. With the total number of 606 glyphs, Brighten is the perfect blend of elegant and casual. Brighten is equipped with plenty of OpenType features. Uppercase letters can alternate between at least two or three different forms and lowercase letters have leastways four choices more to avoid repetition. These effects include start and end forms of lowercase letters, which are automatically substituted in at beginnings or ends of words. To activate the optional glyphs, you may click on Swash, Contextual, Standard Ligatures, Stylistic or Discretionary Ligatures buttons in any OpenType savvy program or manually choose the characters from Glyph Palette. Also, there’s some ornaments designed to support the font (access the ornaments through the Glyph Palette). The Brighten family font might be the choice to use on creating headlines, logos & posters for branding and packaging purposes. - Mundbind NL by Hanoded,
$15.00I just visited my good friend Jakob Fischer from Pizzadude.dk in Denmark. As always we talked fonts, drank coffee and walked endlessly through Copenhagen, the city where he lives. We thought it would be a fun idea to each create a font from a handmade sign we saw in the city. We only had like 7 glyphs to work with, so the rest was up to our imagination. We also thought it would be nice to give the fonts a similar name. Mundbind means mask in Danish. When you Google translate it, it will give you the wrong translation (it will say 'mouth piece'), so trust me on this one! My font is called Mundbind NL - where the NL stands for Netherlands. Jakob will hopefully call his finished font Mundbind DK - where the DK stands for Denmark. Mundbind NL comes with a monster load of diacritics (including Vietnamese) and two alternate glyphs for the lower case letters that will cycle as you type. - Espinosa Nova by Estudio CH,
$-Espinosa Nova is a revival based on the types used by Antonio de Espinosa, the most important Mexican printer of the sixteenth century and very probably the first punchcutter anywhere in the American continent (1551). In 2010, its main fonts were awarded two certificates of excellence: one by TDC2 (Type Directors Club Typeface Design Competition), one by Tipos Latinos (Biennial of Latin American Typography). According to Robert Bringhurst, it is “an unusually intelligent family of type, reaching back to one of the most exciting moments in typographic history and reaching forward to the typographic future”. All of the fonts intended for setting text include small caps, five sets of figures (oldstyle and lining, both proportional and tabular, plus tabular small caps), many f and long s ligatures, and capital sharp S (U+1E9E). In addition, the Capitular fonts allow to create interesting effects by overlapping layers. This family feels very comfortable in books, but it can be used everywhere a touch of classic & elegance is required. - Ribbons by Positype,
$20.00Ribbon type. Holy grail of complex-lettering-turned typeface or an elusive Loch Ness monster that is often teased, possibly seen in the wild, but never confirmed? From the amazing lettering artist and author Martina Flor and masterful type designer Neil Summerour, comes the aptly named Ribbons. Ribbons is a sincere and well-conceived approach to providing a reliable solution to ribbon and ribbon-styled type for creative professionals when a lettering artist just isn’t available. Ribbons provides both flat and ‘folded’ options with the Regular and Fold styles, but then raises the bar with separate layer styles that will allow you to easily create the elegant back and forth movements produced with ribbon-style lettering we have all come to appreciate. These layer options are provided in both ‘smooth’ and ‘pleated’ connected styles. Flor and Summerour didn’t stop there. Each typeface was expanded with a number of stylistic alternates, additional swashed and flourished letters, ligatures, and even more in order to provide as many decorative options as possible to the creative. To round out the nine fonts available in the typeface and to ‘put a bow on it’, they’ve added a separate Shadow style and two different color fonts (available exclusively with family purchases). - Hello Blushberry Script by Great Studio,
$14.00Allow me to introduce Hello Blushberry - Font Duo is a playful script containing many choices of alternative characters to choose from as well as ligatures that look natural to add to the authenticity of letters. A collection of strange and initial swash tips is also included to add finishing touches or fill the design space in your type design. Hello Blushberry a modern handwriting fonts, loaded with awesome opentype features, and full alternative upper and lower case character sets. make custom letters a dream thanks to all the extra decorative choices you can enter for beautiful and unique customizations - swash, endings, alternative letters and ligatures all make it the prettiest little thing since tutus and tiara. Designed to work harmoniously, this duo font consists of super fine and casual signature scripts and a complete and clean set of all sans serif letters. Sans Serif fonts consist of two outline fonts of different weights, and a regular version. Layer them with different colors and turbidity to get a million different views. This font is perfect for branding, logos, web and editorial design, branding, prints, invitations, crafts, quotes, and more. Includes Files: • Hello Blushberry Script • Hello Blushberry Script Capitals Need help? If you need help or advice, please contact me by e-mail at Greatstudio92@gmail.com. - LC Tejuela by Compañía Tipográfica de Chile,
$29.00Tejuela (Spanish for “Wood Shingle”) is a neoclassical type inspired by the wooden architecture of the ancient churches of Chiloé, an archipelago in southern Chile; which are World Heritage Sites. This typeface has rough and broken forms but with soft strokes. The neoclassical characteristic of Tejuela is due to the architecture of these temples, which belong to this style but adapted to wood with excellent quality and ingenuity by Chiloé builders using a material available in the area. Therefore, this typeface reflects the tradition of the fonts of that period, but adapted to the coarseness and warmth of the southern wood of the world. Tejuela is useful for extensive texts in literature, history, art and heritage; as also for short and large phrases in headlines according to the occasion. Tejuela has eight variants in Roman and Italic versions, with small caps, Old Style and Lining numbers, ligatures, alternative glyphs, fractions, among other OpenType features; special mention to the capital letters Swash of the italic versions, which serve to generate delicate compositions. In addition, it has two stylistic sets to compose border ornaments inspired by the Chilota Architecture: colonnades and corners, only using the numbers on the keyboard; it is important that the line spacing has the same value as the font. - Vox by Canada Type,
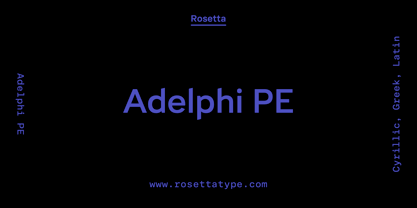
$39.95The original brief for Vox was a extensive monoline typeface that can be both precise and friendly, yet contain enough choice of seamlessly interchangeable variants for the user to be able to completely transform the personality of the typeface depending on the application. Basically, a sans serif with applications that range from clean and transparent information relay to sleek and angular branding. When the first version of Vox was released in 2007, it became an instant hit with interface designers, product packagers, sports channels, transport engineers and electronics manufacturers. This new version (2013) is the expanded treatment, which is even more dedicated to the original idea of abundant application flexibility. The family was expanded to five weights and two widths, with corresponding italics, for a total of 20 fonts. Each font contains 1240 glyphs. Localization includes Cyrillic and Greek, as well as extended Latin language support. Built-in OpenType features include small caps, caps to small caps, four completely interchangeable sytlistic alternates sets, automatic fractions, six types of figures, ordinals, and meticulous class-based kerning. This kind of typeface malleability is not an easy thing to come by these days. For additional versatility, take a look at Vox Round, the softer, but just as extensive, counterpart to this family. - Adelphi PE by Rosetta,
$70.00Adelphi is a geometric sans, redefined for the northern side of the English Channel. Typographic modernism was a late arrival in Britain — due partly to the Second World War and to the strong local type tradition. This delay provided for fruitful divergence, thus modernism was not adored in quite the same way as it had been in Germany and central Europe. It was instead rethought and repurposed against the backdrop of the bleak British weather and postwar social reform – a continental fashion statement reshaped into a more humanist variant. Likewise, when crafting Adelphi, Nick Job reimagined the constraints that defined the geometric sans as a genre. Whereas other typefaces seem overly bound by the rules, Adelphi feels relaxed and approachable. Elementary square and circular shapes are merely implied. A keen observer may notice that the uncomplicated letterforms occasionally reveal a subtle naïveté associated with early Grotesques. Brunel’s bridges and Harry Beck’s tube map spring to mind alongside the Bauhaus and Futura. But Adelphi is by no means nostalgic! It is a contemporary, comprehensive, and durable system with a pragmatic set of features. These include a wide array of weights, ‘uniwidth italics’, and variable extenders that go from tall and flat in Adelphi Text to short and sharp in Adelphi Display, with default Adelphi standing midway between these two extremes. You can set the extenders to your preference in the all-inclusive variable font or use one of the three static fonts that come packed together, priced as a single font. The pan-European support for Latin, Cyrillic and Greek scripts already makes for a vast character set, but Adelphi takes things a step further by including alternate glyphs to satisfy the DIN1450 legibility norm, a range of ordinals that can be used to create specialist compositions in all three scripts and two kinds of fractions and arrows. Play with the alternates or use it as-is. Either way, this understated beauty will carry you through. - Laurentian by Monotype,
$29.99Maclean's is a weekly Canadian newsmagazine with a broad editorial mission. A typical issue covers everything from violence on the other side of the globe to the largest pumpkin grown in a local county. In 2001, Maclean's invited Rod McDonald to become part of the design team to renovate" the 96-year-old publication. The magazine wanted to offer its readers a typographic voice that was professional, clean, and easy to read. Above all, the typeface had to be able to speak about the hundreds of unrelated subjects addressed in each issue while remaining believable and uncontrived. A tall order, perhaps? Now add in that this would be the first text typeface ever commissioned by a Canadian magazine. McDonald, who some have called Canada's unofficial "typographer laureate," took on the challenge. McDonald used two historic models as the basis for Laurentian's design: the work of French type designer Claude Garamond, and that of the English printer and type founder, William Caslon. From Garamond Laurentian acquired its humanist axis, crisp serifs and terminals that mimic pen strokes. Caslon's letters are less humanistic, with a more marked contrast in stroke weight and serifs that appear constructed rather than drawn. These traits also made their mark on Laurentian. Using these two designs as a foundation, McDonald drew Laurentian with the narrow text columns and small type sizes of magazine composition in mind. He gave his letters strong vertical strokes and sturdy serifs, a robust x-height and a slightly compressed character width A tall order, per McDonald's genius is evident in the face's legibility, quiet liveliness and in the openness of the letters. The result is a typeface that not only met Maclean's demanding design brief, but also provides exceptional service in a wide variety of other applications. Laurentian is available in three weights of Regular, Semi Bold and Bold, with complementary italics for the Regular and Semi Bold, and a suite of titling caps." - Open Book ING by Ingrimayne Type,
$9.00OpenBookING is a gimmick or novelty font that has letters on pages of a book. It is caps only and monospaced. The letters on the upper-case keys are on the left-handed pages of an open book and the letters on the lower-case keys are the same letters but on the right-handed pages of an open book. One could alternate upper and lower case keys to get letters on complete books, but the Opentype feature of contextual alternatives (calt) does this automatically. Several previous typefaces from IngrimayneType used the calt feature to alternate shapes that fit together in an interlocking pattern, such as alternating concave and convex shapes. OpenBookING uses the calt feature in a different way, to alternate two halves of a symmetrical shape. To provide two copies of numbers and common symbols, some non-alphabetical characters are unavailable because their slots were taken by the second form of the number or common symbol. If stylistic set one (ss01) is turned on, spaces are replaced with empty pages. This may leave you with unwanted spaces at the end of lines, and to eliminate them, turn off the feature (or change the font) for these spaces. The empty pages can be used in a layer to add color to the text. There is also a second set of empty pages with a filled page that can also be used in layers. (See poster for examples.) These pages are on the (logicalnot multiply) and (register divide) characters for the first set and on the (ordmasculine ellipsis) and (macron trademark) keys for the second set. Finally, OpenBookING has a large set of accented characters if anyone should need them. The letters used on the books were derived from the font Myhota-Bold. For a related typeface of letters on book covers, see NewLibrary. OpenBookING has limited uses and is priced accordingly. - Mundo Serif by Monotype,
$50.99With designs drawn specifically for comfortable reading in everything from on-screen digital content to print in periodicals and books, Mundo Serif is ready to take on just about any project. Carl Crossgrove drew the suite of typefaces to complement his Mundo Sans family’s classic humanistic design traits – and added a subtle modern influence. Restrained stroke modulation, generous counters, commanding x-height and tall ascenders ensure that content set in Mundo Serif is both legible and easy on the eyes. While primarily designed for text copy in print and on screen, Mundo Serif becomes a powerful display type tool in the lightest and boldest weights. Headlines, navigational links and banners are naturals for this versatile collection of typefaces. Mundo Serif is a large family. Nine weights, each with an italic companion, enable precise typographic tuning. Captions, subheads, pull quotes and long-form copy can be melded to create a welcoming page of modulated text. For best results in digital environments, skipping a weight – or even two – ensures hierarchical clarity. Crossgrove did extensive testing of Mundo Serif to ensure the best possible on-screen readability. To further guarantee optimal digital imaging of the family, he gave the design generous inter-character spacing and slightly expanded intricate characters like the lowercase a and g. If the goal is diversified or multi-platform branding, look no further than Mundo Sans. The two designs harmonize with each other perfectly in weight, typographic color and proportion. Both designs benefit from large international character set that includes support for most Central European and many Eastern European languages. For a stronger contrast, pair Mundo Serif with virtually any sans serif grotesque design. Crossgrove has designed a variety of typefaces ranging from the futuristic and organic Biome™ to the warm, clean lines of the Mundo Sans. His work for Monotype also often takes Crossgrove into the realm of custom fronts for branding and non-Latin scripts. - P22 St G Schrift by IHOF,
$39.95P22 ST.G Shrift is a font series based on the type designs of Stefan George with an italic version designed by Colin Kahn. Stefan George (1868-1933) was a German poet who led the revolt against realism in German literature. All of his works were privately published and the typefaces that were used reflected his neo-classic and anti-industrial (progessive) aesthetics; oftentimes consisting of his own hand lettering designs. The original font was cast in 1907 by a small foundry in Germany and was used primarily for the works of George as well as other books including a monumental edition of Dante's Divine Comedy. The ST.G Shrift Fonts contained in this set are derived from 3 known variations of the original roman typeface, St.G., found in various books published in Berlin in the early 20th century. ST.G Shrift One contains the most idiosyncratic characters, while ST.G Shrift Two uses more familiar characters as well as a redesign of characters including the t and the k to be more in keeping with modern san-serif designs. The OpenType version of the roman contains both one and two and expands on them by including central European characters, small caps, and small caps titling figures. The Small Caps titling figures are derived from the first version of the typeface. Below is a features list (accessible through the type palette in Adobe programs) and their functions: ST.G Shrift Opentype Features: Small Caps: Changes Lowercase to Small Caps Titling Figures: Changes Uppercase to Titling Caps, and Small Caps to Small Caps Titling Figures Contextual Alternates: Changes Character Set to match ST.G One and changes Small Caps to Titling Small Caps Ornaments: Changes < > and ? (greater, less and bullet) to ornaments ST.G Shrift Italic is an art nouveau version of the roman. The OpenType version includes central European characters, small caps, titling caps, titling small caps and ornaments. - Just Shoes And Purses by Outside the Line,
$19.00 - Boxy Code by Just My Type,
$15.00In the late 60’s, one of the best art publications in the country was Motive magazine, published (amazingly) by the United Methodist Church. Filled to the brim with poetry, essays, line drawing and woodcuts, it also featured some cutting-edge typography. Boxy/Code is based upon my memories of woodcut typography from that great magazine. Since Boxy/Code ’s lowercase consists of the uppercase’s negative spaces, it’s easy to combine the two with Layer Styles in Photoshop in order to achieve the effect I used in one poster above. It also works great if you use a well-known text as a background. This new version is totally redrawn and features all the Latin-accented letters. Uppercase consists of black capitals in boxes; lowercase features the negative spaces of those boxed capitals. Uppercase and lowercase line up exactly for 2-color effects. - Beat Fool by PizzaDude.dk,
$15.00Beat Fool is my latest layered font. I love making layered fonts, because the possibilities are almost endless! Play around with transparency and your favourite colorschemes and patterns to create awesome effects! Beat Fool comes in two layers that plays well together. One layer is solid and can be used for shadow, fill, texture or other creative parts of your design. The second layer is the "Regular" one - the outline that made the basis for the font. I wanted the handmade and handwritten brushstrokes visible, to keep the flaws which makes the look more authentic. Every letter has 4 different versions, again to make things more natural and kind of random! Both layers can be used alone or as described, together - and since it has multilingual support, you can be creative in all kinds of languages! :) - Vinneta by Dima Pole,
$27.00Vinneta is a direct italic font. Its contours and graceful, and precise. Vinneta has a huge number of alternative variations of the glyphs, 20 stylistic sets, it allows you to create a variety of compositions. In addition Vinneta has 17 OpenType features, including oldstyle numbers, swashes, contextual alternates, historical forms, standard ligatures, discretionary and contextual ligatures, localized forms, stylistic alternates, and more others. For convenience here are two faces, one with stylized capitals (they are different from swashes), in another - classic capitals. Vinneta has characters of all European and Slavic languages. "Vinneta" it is an ancient city of the Venedi (Wends), the legendary highly developed Slavic-Aryan people that lent its name to Venice city, lake Bodensee in southern Germany, the land of Wendland in Lower Saxony; and besides, Lithuanians and Estonians even today, this name referred to the Slavs (Veneja and Vene). - SF Article by Sultan Fonts,
$40.00About Sf Article font family: Sf Article is An Arabic and Latin typeface for desktop applications ,for websites, and for digital ads. The main types of Sf Article font family weight are regular and bold. The regular weight is perfect for reading, it is helpful during long reads, Bold Sf Article styles are designed to draw attention to short phrases. The Sf Article font family is characterized by short heights and dynamic stretching of letters through the paragraph, where the space In the line is automatically filled. In Sf Article font family, we have developed two italic fonts: regular and bold, to help with the diversity of stylistic expression in the Article, document and research work. Sf Article typeface comes with many OpenType features including stylistic sets. Designer: Sultan Maqtari Design date: 2021 Publisher: Sultan Fonts - Merchande by Tom Chalky,
$19.00Introducing the 'Merchande' Font Trio Inspired by a variety of midcentury typefaces, the Merchande trio was designed to add pizzazz to your branding, packaging, advertising, and print projects. What's Inside? The serif is fantastic for headlines, logos, and anything that needs to grab attention. Its tall, condensed, and confident appearance is a great head-turner, made even better when combined with the two below. The script is perfect when a premium touch is needed for your work. Its use immediately adds a charming, personal quality. The best part, it's wonderfully legible in any size. While the sans works fantastic as a large display font, it truly shines when used for its intended purpose. Small text. Evidence of this is scattered throughout the presentation images. Tip: Increase the space between the letters (tracking), it looks awesome. Thanks for looking! Tom - Softly Bright by Ditatype,
$29.00Introducing Softly Bright, a dynamic font duo that effortlessly combines the contrasting styles of sans-serif and brush fonts. The sans-serif component of this font is a testament to clean lines and modern minimalism. Its characters are created with precision and defined strokes, offering a sharp and sleek appearance that exudes professionalism and readability. On the other hand, the brush font in Softly Bright adds an expressive touch to your designs. It embodies the authenticity of hand-lettered strokes, with each character bearing the organic irregularities of brushwork. This brush font retains the proportions of the sans-serif, ensuring that the two styles harmoniously coexist. Softly Bright fits in headlines, logos, posters, flyers, branding materials, print media, editorial layouts, and many more designs. Find out more ways to use this font by taking a look at the font preview. - Jetlab by Swell Type,
$15.00Jetlab is a typographic time machine that drops you squarely into the techno-futuristic optimism of the 1960s, 1970s and 1980s! While certain weights may conjure familiar space race-era logos from the sci-fi movies, board games, sports teams, new wave bands and sneaker brands of the late 20th century, the complete 45-weight Jetlab font family is loaded with modern features to power your retro-futuristic designs with near-infinite versatility. Features: 45 weights provide widths from squeezed to stretched and weights from light to heavy, plus reverse-stress (that's thick horizontal strokes with thin verticals) high, medium and low crossbar options upper and lowercase letters provide two distinct styles a four-axis variable font provides precise control of width, vertical & horizontal weight, and crossbar height 500 glyphs support 223 languages, including Western & Central Europe and Vietnamese - P22 Dearest by IHOF,
$24.95Dearest is a distinct flowing script based on handwritten characters found in a 19th Century German book chronicling a history of the Middle Ages. Originally released in 2001 as a set containing two styles, Script and Swash, Dearest is now expanded in 2014 as a pro font with several hundred new characters including support for Central European, Cyrillic and Greek languages. Other Opentype features include ligatures, fractions and figures, Roman numerals, alternate letterforms and more swashes to expand the possibilities of this designer-friendly font. In addition to the Dearest Pro font, a new companion font has been added- P22 Dearest Alternates. The characters contained in this font are part of the pro font, but are also designed to be used with Dearest Script and Dearest Swash and is intended for those who have applications that do not support Opentype features. - Otama by Tim Donaldson,
$49.00From the dainty light weight through to the striking UltraBold, Otama raises the bar to a new level of dangerous sophistication. Although easily classified alongside Modern typefaces such as Didot and Bodoni, Otama was purposely developed with minimum reference to these two visual heavy weights. In search of something more than a mere historical revival, Otama instead draws proportional reference from popular 20th century Transitional and Garalde typefaces with visual inspiration coming from calligraphic studies. Many characteristics from Tim Donaldson’s 2010 display face Pyes Pa were directly passed on in execution of Otama — The shoelaced k, e and a being the most obvious examples of this family relation. Refined over 2 years with well over 8,000 characters over 28 styles, Otama certainly deserves its place as a comprehensive and versatile typeface in any designer’s font library.