1,960 search results
(0.036 seconds)
- Camplones by Miracledsign,
$8.00Camplones is a handwritten font that accentuates the style and curve of the hand when inking the ink on the paper by perfecting the shape of each character so that Camplones looks very beautiful when applied in a sentence. Camplones is specially shaped and made so that users feel the touch of a hand that lives in the character of the letters so that it has tremendous value when used in your templates, game fonts, wedding invitations or sales products which will surely be very attractive to consumers when they see it and will definitely love it. make the product look more elegant and will increase the selling value of your product. - Blaster by Mozatype,
$19.00BLASTER is a casual, fun display font, created by using a brush pen. It has an urban and trendy feel and it will most definitely fit a wide range of designs. This font is perfect for brand announcements, packaging, quotes, branding, advertisements, blogs, logos, invitations, and more! This font is PUA encoded which means you can access all of the stunning glyphs and swashes with ease! It also features a wealth of special features including alternate glyphs and ligatures. What’s Included : – Works on PC & Mac – Easy to use ( Installations ) – Easy Convert to webfont – Compabilty Windows, Apple, Linux, Cricut, Silhouette and Other cutting machines Thanks for downloading, and I hope you enjoy it! - Wilderness X by Enfeeltype,
$15.00Wilderness X is a font name that has a very wide wilderness concept. This font has a very large variety of characters, including isolated characters with strong definition and small text. It is also a font which can be used as a random display font. There are also many other options, such as: different stroke thickness and size, change the glyphs and so on A wilder a wilderness, the more rewarding the journey...I love the idea of exploring and staying on the edge, getting dirty and making my path is challenging. Wilderness X is not a bland font but has a bit of badness in it which makes it more interesting and attractive. - Arista Pro by Zetafonts,
$39.00Arista Pro is the definitive version of the successful Arista typeface, designed by Francesco Canovaro, first released in 2007 as Arista Z and then reissued as Arista 2.0 in 2010. The pro version of Arista features the geometric and soft approach of the original typeface but comes in a full range of weights and two alternate versions (Arista Pro Regular and Arista Pro alternate version). The typeface has been expanded with the inclusion of Greek and Cyrillic alphabets as well as an extended range of latin characters. A companion icon typeface, Arista Pro Icon, has been developed, allowing for variable-width monoline icons that can be used to faultlessly match the typeface line width, up to semibold weight. - Spellcaster by Comicraft,
$19.00Raven hair and ruby lips, it may have been a trick of the light but I'm sure sparks flew from her fingertips. I definitely heard echoed voices in the night, of a restless spirit on an endless flight. If I remember correctly she held me spellbound in the night, with dancing shadows and firelight. Yes, I think I did see a crystal ball on the table, showing the future, the past and I did drink the potion she offered me, when I really should have gotten out of there fast. And that's my story and I'm sticking to it, your honor. It was that girl with the white hair, I'm telling you. She has my wallet too. - Festabe by PizzaDude.dk,
$20.00It's time for a party! A party with monkeys, or a party AS monkeys! :) The danish term "Festabe" is a partyanimal, and definitely in a positive way! And that's the spirit of this font! It has that happy attitude, that could boost your designs in a happy and positive way. Besides legibility, the font is superlegible, even at very small sizes. But try looking at the letters at a LARGE size, and you will notice the smoothness of each letter! To ensure the letters don't get too alike, I've added several (slightly) different versions of each letter. In fact, every letter has 5 different versions, and these automatically cycles as you type! - László by Just My Type,
$20.00We count three inspirations for the László font family. The upper case was inspired by Yomar Augusto’s amazing font Unity, used on last year’s German World Cup Team jerseys; the lower case from a few letters a poster for a Bauhaus show. The name László is an homage to László Moholy-Nagy, peerless Bauhaus designer and teacher. The László type family is stripped down to the typographic core, lean, clean and definitely machined, at home in either a formal or casual setting, i.e. you can take László anywhere. Inspired by watching the World Cup and the German Team’s jerseys. Very clean, simple, Bauhaus-style design, European and highly legible. Usage recommendations Automobile ads, anywhere a European feel is desired. - Annonce by Canada Type,
$24.95Annonce is a digitization and expansion of a 1912 Johannes Wagner Foundry classic called Aurora Grotesk, which also circulated later on in metal under the name Annonce. Bold, extended and clear as a bell, Annonce stood out as the definite big sign font long before the Helveticas of the world. With angled cuts on some of the letters, it also shows humanistic traits that make it more appealing than any other face in its genre. The Annonce set comes in two fonts, a regular and an italic, and includes a very large character set that accommodates almost all Latin-based languages, including Turkish, Baltic, Celtic, Maltese, Esperanto, and the languages of Central and Eastern Europe. - Videomax by PizzaDude.dk,
$16.00Videomax looks like something from the future - perhaps even something from a future where the world lies in ruins and is about to be taken over by hostile aliens. The worn letters represent the decades of war against the computers...or the aliens...or maybe the letters comes from a sign of a computer company from the eighties, which was recently found in an abandoned place. The speculations are many, but one thing is definitely true: Videomax got that grungy / computer / worldwar feeling! Write your text, and watch how the randomness of letters make your text look really good. I've put it 4 different versions of each letter, which makes it look really nice and worn! - Novecento Sans by Synthview,
$-This is of Novecento Sans, a font family inspired by European typographic trends between the second half of 19th century and first half of the 20th. It looks rational and geometric. However, it is optically corrected and balanced. NEWS: you can add a layered effect with Novecento Carved as top layer. This font face is designed to be used mostly for headlines, visual identities or short sentences, both in big and small sizes. Lighter faces provide a more contemporary and design look and feel, while the bolder ones definitely look retro. Novecento Sans family comes in 32 styles, speaks 76 latin based languages, has 590 glyphs and 16 stylistic opentype features for advanced typography. - Nomos Sans by Identity Letters,
$45.00What is a brutalist typeface? The exact definition is anyone’s guess. Regardless, the Nomos superfamily is our take on the genre. Like the eponymous architectural style, Nomos is raw, direct, and honest. Its unrefined aesthetics reveal an orderly construction that is as firmly rooted in classic modernism as in the internet age—with simple, functional letterforms and the blunt convergence of diagonal and vertical stems. The Nomos Sans subfamily is a low-contrast neogrotesk with 18 styles and a set of 1000+ characters. A confident choice for fashion and finance, for apps and advertising: humble and expedient in body text, vigorous in display sizes. Has extra poise when paired with Nomos Slab. - Quintus LeadedGlass is a font that exists in the realm of artistic imagination, embodying an exquisite blend of classic elegance and contemporary flair. Its design is inspired by the intricate crafts...
- Neue Plak by Monotype,
$57.99Originally designed in 1928, Plak is something of a lost gem in the type world. Despite being drawn by Futura creator Paul Renner, it never achieved the same popularity and spent decades lacking a much-needed digital revival. Monotype designers Linda Hintz and Toshi Omagari have taken its existing three weights and, after extensive research into the original wood type, extended them into the vast Neue Plak family. The typeface is available in 60 weights that stay true to Renner’s intentions, and offer the same blend of “quirky” details and “German stiffness” – as Hintz describes it. The design is an unusual mixture, bringing together a defiant outer appearance that’s counteracted by more playful details found in the lowercase r, and the large dots of the lowercase i. Other distinctive details include open or strikethrough counters, and a set of hairline widths that reduce Renner’s original design to its bare bones. Neue Plak’s display weights are crying out to be used in editorial, on packaging or in logos, while its text weight works well in both print and digital environments. Neue Plak Text Variables are font files which are featuring one axis and have a preset instance from Thin to Black - Krellon by Nathatype,
$29.00Krellon invites you to step back in time and embrace the elegance of the past with its vintage style. Rounded shapes define each character, creating a sense of approachability and friendliness. What makes Krellon so special is its subtle, textured appearance. The font carries a delightful roughness that adds authenticity to your text, as if each letter has endured the test of time. Beautiful ornaments are included as a bonus. Krellon fits in headlines, logos, branding materials, and many more. - ALS Ekibastuz by Art. Lebedev Studio,
$63.00ALS Ekibastuz is a contemporary urban-style typeface extremely suitable for periodicals and advertising. It has defined, open, clear-cut letterforms and modern proportions. Originally designed to work well for headings, Ekibastuz was developed further to give a distinct energetic feel when used at large sizes and be highly readable and neutral at small sizes. It consists of six font styles and offers a wide choice of weights, which is useful for creating contrast between boxes of text on a page. - P22 GD&T Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing by P22 Type Foundry,
$24.95Geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T) is a system for defining and communicating engineering tolerances. It uses a symbolic language on engineering drawings and computer-generated three-dimensional solid models that explicitly describe nominal geometry and its allowable variation. This highly specialized symbol font is designed specifically to be used by engineers to describe CAD produced outside the CAD environment. Included is a chart featuring character names and keyboard placement. Complies with ASME Y14.5M-1994. Updated to include 2009 addition of ‘unilateral’ symbol. - SosaBravo by Alejandro Yñigo,
$12.00“SosaBravo” is a font with a unique design... Its shapes are defined only by straight lines and the compositions that can be made communicate a casual and aggressive style that cannot be ignored. The structure of its glyphs and its anatomical details will transmit dynamism and freedom in each design where it appears. It is a font inspired by the work of the Cuban artist Manuel Alfredo Sosabravo, with his own very personal, pictorial and aggressive style, as this font is. - Astroviz by Jehoo Creative,
$18.00Astroviz is more than just a font it's a design statement. Its deep ink traps are the defining feature that sets it apart, making it an ideal choice for creating captivating and memorable headlines that demand attention and leave a lasting impression. While the ink traps are a prominent feature, Astroviz maintains an elegant and curvaceous design overall. Its letterforms are fluid and harmonious, with a balance of thick and thin strokes that give it a luxurious and sophisticated appearance. - Schola Serif by StudioJASO,
$56.00Schola Serif is a neo classic serif font that reinterpret the classic Latin style structure and expression in a modern and intriguing way. Schola Serif looks sharply defined, giving clear-cut impression. It features sharp serif and details and presents its own distinctive character when used in title or sub headline or written with over 16pt. Font with 5 different weights, over 60+ languages, 9 OpenType features. It really does work in everything ranging from editorial design, graphic, and even integrated branding design. - Mighe Huntera by Namara Creative Studio,
$20.00Retro modern serif typeface inspired by the typography of the ’90s, which exudes an irresistible sense of nostalgic and timeless charm. Each character showcases sharp, defined serifs that effortlessly merge with thick, prominent strokes, creating a harmonious balance between boldness and elegance. Features : Full Set of standard characters and punctuations. Alternates, Ligatures & Multilingual Support PUA Encoded | no special software needed to access extra characters. We recommend using a program that supports OpenType features and Glyphs panels like Adobe Apps, Corel, etc. - Hyperon by ParaType,
$30.00Hyperon is a text typeface, which is especially useful for math and physics literature. Its nature is defined by austere and humanist features that show the most in italic. The typeface includes weights from Regular to Black and widths from Condensed to Semi Expanded. What stands out for Hyperon is the extended character set, with added Greek and lots of mathematical signs. Some styles have small caps. The typeface was designed by Natalia Vasilyeva and released by Paratype in 2020. - 8th Avenue by Our House Graphics,
$16.00Inspired by the strange, blocky lettering on the sides of a set of a set of plastic kitchen containers in my childhood home, 8th Avenue is a sophisticated, somewhat syncopated font with a retro look and feel that at the same time brings a very modern attitude to your design. 8th Avenue works well as display font for packaging, headlines and logos. Those pastel turquoise plastic boxes from the early 1950s, with white screen printed letters reading FLOUR, SUGAR, COFFEE etc. on one side were a simple quiet presence in our home back then and for decades after. Seeing them, even that soft blue-green colour felt like home. SUGAR, the soul survivor of that set has become one of those mundane items of daily life that somehow become simple icons of another time, ripe with memories. Obviously I had to make a font. September 2014 - ABTS Crestwing by Albatross,
$19.95ABTS Crestwing is a unique initial font with extraordinary flexibility and beauty. There are 5 wing styles to choose from. The wings are accessed through typing numbers. The 5 pairs are: [1, 2] [3, 4] [5, 6] [7, 8] & [9, 0]. The odd numbers in the pairs will give you a left wing, and the even numbers will give you a right wing. The letters are separated into upper and lowercase. Uppercase has a crest point, the lowercase does not, giving you the ability to string letters together to form words and phrases, and place the tip of the crest above the letter of your choosing. Optional endcaps are available using the brackets on your keyboard "[, ]." This allows you to cap off a word if you wish not to use a wing to do so. Crestwing is both beautiful and unique, and works best at large sizes. - ITC Migrate by ITC,
$29.99George Ryan's ITC Migrate is a highly condensed sans serif display face that effectively complements ITC Adderville. Migrate represents what Ryan calls a “more highly evolved version” of a typeface he designed for Bitstream in 1991 called Oz Handicraft. “Both faces,“ says Ryan, “are based on designs of the popular early 20th-century type designer Oswald Cooper.” His inspiration came from drawing samples found in the Book of Oz Cooper, published in 1949 by the Society of Typographic Arts in Chicago. “Oz worked extensively with the sans serif form long before it became popular in the States, eschewing a popular belief of the time that sans serifs were only skeletons of letters.” Where Oz Handicraft was informal and quirky, ITC Migrate has a more restrained feel. “The uppercase characters and figures, in particular, have been reworked,” says Ryan, ”resulting in a more formal and traditional, compressed sans serif typeface.” - Onomatopedia by Comicraft,
$29.00Fans of Comicraft have made a lot of noise (HELP!) about the availability of ready-to-wear, factory surplus sound effects, not unlike those made available over a decade ago in our extremely popular and raucous ZAP PACK. It may sound impossible (WHA--?!), but Comicraft's Sonic Specialist, John JG Roshell, locked himself away (CLIK) in our top-secret SFX lab forming Onomatopoeia at high speeds (FWOOSH) and extreme temperatures (BBRRR), and sounded out over One Hundred (GASP) of the loudest (BTOOM), most intense (UNNGHH), squawkiest (KRAKK), discordant (SPLANGG), dissonant (SQUTCH) -- as well as dulcet and restrained (THWIPP) -- sound effects ever conceived (WOO HOO!) Helpfully arranged in alphabetical order (YIPPEE!), this Library of Onomatopeia -- the ONOMATOPEDIA, if you will (DING) -- is now available for use by the general public. WARNING: Comicraft Sound Effects may explode on contact with skin (AAAH!); please use protective clothing and eyewear when handling the Onomatopedia. - Gill Hebrew by Lerfu,
$55.00Near the end of his life, legendary type designer Eric Gill lived in Jerusalem, and became interested in the typesetting of the Hebrew alphabet and the challenges it entailed. He designed his own Hebrew font which has not (to my knowledge) been digitized before. It is sometimes held up as an example of how not to do a Hebrew font: Gill introduced strange serifs and shapes that were jarring to readers used to more traditional fonts. But it is quite readable, and does start to grow on you after a while; extended text in Gill Hebrew is possible. I've added a set of alternate digits that are based on the shapes of the letters (Gill's digits are pretty standard text figures). I've also made some of the Unicode Hebrew symbols that Gill didn't (e.g. New Sheqel Sign, Alef-Lamed ligature, etc.) and also included vowel-points. - ITC Tempus Sans by ITC,
$29.99ITC Tempus is the work of British designer Phill Grimshaw. He claims that every calligrapher's aspiration is to draw perfect roman capitals with a pen, but admits that this is extremely difficult. For this typeface, Grimshaw used a fountain pen on cheap, porous paper and, of course, the ink bled. The resulting forms are classic but their rugged edges deviate from the perfection of roman type. And Tempus Sans is just Tempus with the serif surgically removed, yet the proportions of the characters work nicely," says Grimshaw. Because of its rough quality, the typeface works best in larger point sizes, yet maintains its characters even in smaller sizes." - ITC Tempus Serif by ITC,
$29.99ITC Tempus is the work of British designer Phill Grimshaw. He claims that every calligrapher's aspiration is to draw perfect roman capitals with a pen, but admits that this is extremely difficult. For this typeface, Grimshaw used a fountain pen on cheap, porous paper and, of course, the ink bled. The resulting forms are classic but their rugged edges deviate from the perfection of roman type. And Tempus Sans is just Tempus with the serif surgically removed, yet the proportions of the characters work nicely," says Grimshaw. Because of its rough quality, the typeface works best in larger point sizes, yet maintains its characters even in smaller sizes. - Ongunkan Lycian by Runic World Tamgacı,
$50.00Lycia (Lycian: 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 Trm̃mis; Greek: Λυκία, Lykia; Turkish: Likya) was a geopolitical region in Anatolia in what are now the provinces of Antalya and Muğla on the southern coast of Turkey, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, and Burdur Province inland. Known to history since the records of ancient Egypt and the Hittite Empire in the Late Bronze Age, it was populated by speakers of the Luwian language group. Written records began to be inscribed in stone in the Lycian language (a later form of Luwian) after Lycia's involuntary incorporation into the Achaemenid Empire in the Iron Age. At that time (546 BC) the Luwian speakers were decimated, and Lycia received an influx of Persian speakers. Ancient sources seem to indicate that an older name of the region was Alope (Ancient Greek: Ἀλόπη, Alópē). Lycia fought for the Persians in the Persian Wars, but on the defeat of the Achaemenid Empire by the Greeks, it became intermittently a free agent. After a brief membership in the Athenian Empire, it seceded and became independent (its treaty with Athens had omitted the usual non-secession clause), was under the Persians again, revolted again, was conquered by Mausolus of Caria, returned to the Persians, and finally fell under Macedonian hegemony upon the defeat of the Persians by Alexander the Great. Due to the influx of Greek speakers and the sparsity of the remaining Lycian speakers, Lycia was rapidly Hellenized under the Macedonians, and the Lycian language disappeared from inscriptions and coinage. - HK Modular by Hanken Design Co.,
$45.00HK Modular stands out as a versatile and adaptable typeface that finds its strength in serving as an impactful display, title, or poster font. Its design allows for effective use in spanning entire pages, highlighting article titles, and designing logos. With a regular cut and rounded-corner design, HK Modular strikes a harmonious balance between sleekness and approachability. This dual nature of the typeface allows it to seamlessly blend sharp, defined edges with a touch of softness, making it suitable for a wide range of design contexts. - Tempestua by Sharkshock,
$115.00Beauty….Style…. Sophistication…. Tempestua is a very chic display font suitable for a variety of purposes. This typeface is defined by wispy thin lines paired alongside broad strokes for maximum contrast. Some of the lowercase letters feature shaved off serifs as well as flattened tops. Elegant curves will keep eyes moving throughout ensuring viewers will be stopped in their tracks. Use Tempestua for a luxury brand logo, magazine, or movie title. This family is equipped with Basic Latin, Extended Latin/ diacritics, kerning, italics, and support for Polish. - Faithful Fly by ITC,
$29.00Faithful Fly is an alphabet of capital letters designed by David Sagorski in 1994. Vital and dynamic, the figures of Faithful Fly dance across the base line. Zigzag strokes and energetic forms define this frolicsome font. Little ovals decorate the figures in different places. A marked contrast between finer and stronger strokes can be seen in all characters and builds the foundation of the unmistakable image of this font. Faithful Fly's fresh, young look makes this font perfect for comics, cartoons and trend magazines. - Vonique 43 by Sharkshock,
$125.00Vonique 43 is a stylish display font designed to stop passerby in their tracks. Curvaceous lowercase members define this font along with a consistently thin line weight throughout. Most are elegantly styled after circles featuring very short descenders and matching the cap height of capital letters. Vonique 43, like its predecessors, was not designed for everyday text, but eye catching logos. It's equipped with support for many different languages including Russian and Greek. Use it for a luxury brand, clothing line, or a company logo. - Myster by Serebryakov,
$49.00Myster is a truly random font — each lowercase letter has three alternatives, that interchange in the set. This makes Myster look alive, hand-crafted, painted for a special occasion, rather than a font selected from a regular type case… Of course, the mystical character of the font defines the scope of its usage — film, gaming and publishing industries. However Myster’s field of application goes beyond them. This font is able to create a desired atmosphere in packaging, children books, magazines, as well as in advertising. - Brenta by Ludwig Type,
$45.00Brenta is a crisp typeface with open counters and compact proportions, its name referring to a range of mountains in northern Italy. Like its namesake, Brenta is characterized by sharp-edged and sturdy forms, but also by its clarity and elegance. Strong serifs, flat and bold shoulders and open terminals pronounce the horizontal and help to guide the eye along the line. Very fine junctures keep the characters sharply defined and create dynamic light traps. Visit this minisite to see the Brenta webfonts in action: http://brenta.ludwigtype.de - Kantor by T4 Foundry,
$21.00Kantor's modular stroke and humanist axis defines it as an old-style 15th century Venetian serif typeface. At the same time, the lowercase Kantor alphabet is relatively compressed and has the vertical stems of a textura blackletter. However, Kantor has distinct, penformed shapes and has also kept all the organic irregularities of traditional handwriting (or punch-cutting, as it were). Kantor is not happy, not sad - but calm and dignified. Perfect for buddhist poems, fantasy video games and antique scrolls to give that "long time ago"-feeling. - Schooner Script by Three Islands Press,
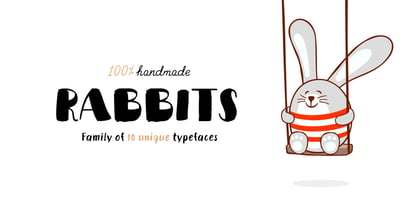
$39.00I happened to mention to the proprietor of an antique barn near here that I'd be interested in any old typewriters she happened to come across. A conversation ensued, the proprietor withdrew into a back room, and she re-emerged with an old handwritten letter, dated 18 Sept. 1825 and spanning nearly three pages. The letter, penned by Samuel Clarke, a Princeton, Mass., pastor, sought donations for the victims of an accident at sea. I thought his script unique, stylistic, and definitely something worth digitizing, so I bought the old letter and took it home. Had to come up with several uppercase characters to round out the set, but the results seem good and proper. Full release has complete character set. - Rabbits by Piñata,
$9.00Rabbits is a super emotional hand-written font family that unites 10 different fonts. We’ve united these fonts with one common theme - childhood. Use these fonts to create any products for kids — children’s books layouts, mobile applications for children, as well as nursery interior design. We’ve given each rabbit a unique name. The names are arranged as the first 10 letters of the Latin alphabet: A — April, B — Bro, C — Chili, D — Dummy, E — Elf, F — Fatso, G— Goody, H — Hyper, I — Idol, J — Junior. Each rabbit has its own character, and you’ll definitely like Rabbits because of that. We’ve used an individual writing tool for every font. All the fonts were created on paper first and then digitized. Now, what’s your favorite rabbit? - Aarde by Scholtz Fonts,
$19.00This is the definitive standard African font. It combines wonderful readability with tremendous panache. The fact that it has a full character set (UPPER and lower case), all punctuation and all special characters, means that it can be used in just about any African design context. If you had only one African font in your arsenal, it would have to be Aarde Black. The name "Aarde" means "earth" and refers to the gutsy, earthy character of the letterforms. It includes a full character set: characters for English, French, Italian, German, and Portuguese. The numerals are mono-spaced, and are very readable so that they will line up correctly in columns of figures. The letters of the alphabet are correctly kerned so that they appear correctly in text. - Occam by Veil of Perception,
$20.00Occam is an informal calligraphic script face. The letter forms were drawn and constructed rather than penned or brushed but reflect a definite flat pen influence. The ascenders and descenders incorporate an abstract implied loop form. Some curves that would normally be round are pointed and some transitions that would normally be sharp and pointed have been made round. A few exit strokes curve back instead of moving up and out for a little different look. This font could be put to good use as a contrasting style combined with sans and serif faces in applications such as newsletters, brochures, invitations and annual reports. It could be used for heads, subheads, pull quotes, drop caps and as a title font for covers.